What is happening in professional art practice? What are my students interested in? What are the latest theories on learning and teaching? One could argue that these are the three essential and recurring questions to which every art teacher should have an answer. Over the course of my four-year research project I have focused primarily on tackling the first two questions, working within the theoretical framework of authentic art education – a framework that is in itself a partial answer to the third question. Authentic art education was introduced to the Netherlands by Folkert Haanstra1. Emerging from a socio-constructivist theory of learning, authentic art education rests on the founding belief that art education is put to its best advantage in complex, lifelike learning situations that, on the one hand, connect to students’ interests, and on the other, to developments in the professional art field. This entails that the content matter and pedagogy of art education are acknowledged as inherently dynamic, which challenges art educators to align existing curricula and pedagogies with present-day visual production and learning forms.
In the course of my study I examined current art practices among amateurs, young people and artists, with particular emphasis on the influence of new technology on these practices. The young people and amateurs were incorporated into the research project by studying informal creative networks formed by graffiti artists, musicians, fan-artists, cosplayers and other -communities.2 The practices of professional artists were -collated both through a literature study of socially engaged, collaborative art practices, and through interviews with Pilvi Takala, Jeanne van Heeswijk, Aram -Bartholl, José Antonio Vega Macotela, The Propeller Group and other artists and collectives.3
Based on the typical characteristics that I distilled from contemporary informal and professional creative work practices, I formulated a number of recommendations that provide an update to Haanstra’s original theoretical framework. Below I set out a number of these recommendations, which are compared with the characteristics of traditional art education. It should be noted that the characteristics of traditional art education are merely used as a counterweight to the position I have taken. I do not suggest that there are no other -innovations in art education going on. The recommendations set out below are directed primarily at those teaching visual arts subjects in secondary schools, but they can also be viewed from the broader perspective of arts education as a whole.
Encourage students to establish meaningful connections between professional art, popular culture and real-world local and global issues.
Young people develop expertise and artistic preferences based on specific areas of interest derived from popular culture. Their cultural production is not aimed solely at artistic development; it is also fuelled by an urge to communicate or to explore certain problems or interests. This broad approach is also evident among many contemporary artists who examine social issues through their work. It is possible to create an individually significant learning path for students by allowing them to respond in their work to topical issues (whether remote or close at hand), and to source inspiration from both popular culture and ‘high’ art. In traditional art education, learning is mostly focused on traditional ‘high’ art; popular culture and personal reflection on social issues are generally viewed as less relevant.
Stimulate interdisciplinary production
Young people and artists alike often mix a variety of media and art disciplines to express themselves. Their work is often not driven by medium, but by ideas. The rise of easily accessible multimedia technology has made a huge contribution to this development and stimulates the potential for merging existing art disciplines.4 Traditional art education is often presented in the form of mono-disciplinary, ‘analogue’ subjects such as drawing and handicrafts.
Stimulate longitudinal artistic research
There is a tendency among artists to embark on long-term research-oriented projects that produce a series of events and products rather than a single art object. Work that young people produce outside school typically draws on a long-term fascination and immersion in a single particular subject. Creative production and critical reflection are parallel and reciprocal processes in art, which are stimulated in an inquiry-based curriculum.5 A process-based pedagogy grants artistic processes as equally important as final products and acknowledges creative production and critical reflection as parallel and reciprocal processes in art education. Final products are seen as temporary stages in an ongoing artistic and learning process.6 Teachers in an authentic curriculum strive for long-term assignments and try to avoid lessons that are ‘crumbled’ into a traditional school timetable. Traditional art education is strictly product-oriented and typically involves only short-term assignments.
Encourage collaborative production as well as online and off-line interaction with people outside the classroom
The era of the artist as a lone genius has passed – if indeed it ever truly existed. Artists and young people alike use networks and collaborative productions to share expertise and experience and to utilize various skills. Collaboration beyond the classroom offers opportunities to push the boundaries between a learning community and real world communities of practice, and enables students to establish interactive relationships with people with different backgrounds, ages and expertise than are available in class. On- and offline collaborative interaction increases opportunities for multicultural learning, as it intensifies the cultural diversity of the learning community.7 Traditional art education is usually based on individual expression and one-to-one teacher supervision. There is little opportunity for cooperation and interaction with others.
The mastery of analogue and digital techniques is instrumental rather than a goal in itself
Technical skills increase the potential for creative expression. However, young people and artists generally learn these techniques as part of the creative process, driven by the urge to make meaningful work. Learning processes become less significant when technical improvement and the development of ideas are detached from each other.8 I argue that the students’ conceptual development can both include and reinforce their advancement of technical and media skills. The improvement of specialist artistic techniques is more relevant for students who understand what art is about and who know how to link those skills to their personal, artistic concepts. Traditional art education often embarks from the isolated acquisition of techniques and skills, with students only experimenting with creating personally meaningful work in later years.
Sharing, copying and remixing are seen as artistic processes
Art critic Claire Bishop points to selection as a key activity in contemporary image production. The search for and recycling of existing imagery and audio material plays an important role in the practice of contemporary artists, and it is also a prominent feature in the informal artistic production by young people and amateurs. The availability of the Internet (the archive) and digital technology (sample and remix tools) are important stimuli for these developments. In traditional art education, the recycling of existing imagery is often discouraged because students are required to think of ‘something original’.
The findings above informed an updated pedagogical framework for authentic art education, which was implemented and evaluated at different schools. The experiences of 20 teachers and 300 students with the framework of authentic art education will be presented and discussed in my forthcoming dissertation. The study aims to provide an insight into design-based methodologies that can be applied to reduce the gap between formal art education and contemporary real world visual practices.
Wiederabdruck
Dieser Text ist eine abgeänderte Version von: Emiel Heijnen, „Artistic Strategies in the Network Society”, On Air, 5, 2012, S. 26–27.
1.) Folkert Haanstra, De Hollandse Schoolkunst. Mogelijkheden en beperkingen van authentieke kunsteducatie [Dutch school art. Possibilities and limitations of authentic art education]. Utrecht 2001.
2.) Kerry Freedman, Mira Kallio-Tavin, Andrea Karpati, Lazlo Papp “Visual Culture Learning Communities: How and What Students Come to Know in Informal Art Groups”, Studies in Art Education, 54 (2), 2013, pp. 131–143.
3.) For two examples for works of artists Emiel Heijnen collaborated with, please follow the QR code and find: “Michael Jackson” by IVES.One, (2009) and “Intercambio 55” (2006–2010, from: Time Divisa) by Jose Antonio Vega Macotela. IVES.One is a street artist from Amsterdam. Heijnen interviewed him in 2011. He has never studied art, but learned everything as part of the graffiti scene. In 2009 he was planning to make a stencil of Michael Jackson holding hands with a small boy. When Jackson suddenly died, IVES.one decided not to use this critical image but to honor him through a stencil of the young Michael. This image received a great deal of publicity and still appears in the public space of Amsterdam.
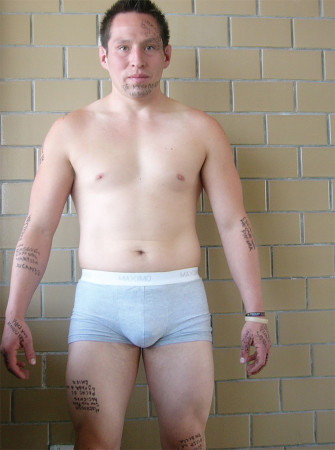
Emiel Heijnen interviewed Mexican artist José Antonio Vega Macotela in 2012. Time Divisa (Time Currency) is the exchange project Vega Macotela realized in collaboration with the male inmates of the overpopulated Santa Martha Acatila prison in Mexico City. Over a period of four years, Vega Macotela visited the prison weekly, encouraging the prisoners to participate in a time exchange experiment. The artist offered to perform tasks for the inmates outside the prison and in return they would have to complete small assignments for Vega Macotela. The project consists of extensive documentation of objects, drawings and photos. This photo shows a prisoner who Vega Macotela asked to mark each scar on his body with an explanation of its origins. In return Vega Macotela attended the birthday of the prisoner’s mother.
4.) Lev Manovich, Deep Remixability. Remix Theory. 2006, S. l. http://remix-theory.net/?p=61 [June 10, 2010]
5.) Kerry Freedman, Patricia Stuhr, “Curriculum change for the 21st century: Visual Culture in Art Education”, in: Elliot Eisner, Michael Day (Eds.), Handbook of Research and Policy in Art Education, Mahwah, N J 2004, pp. 815–825.
6.) Talita Groenendijk, Marike Hoekstra, Robert Klatser, Altermoderne Kunsteducatie: theorie en praktijk [Altermodern Art Education: theory and practice]. Amsterdam 2012.
7.) Sanna Järvelä, Simone Volet, Hanna Järvenoja, „Research on Motivation in Collaborative Learning: Moving Beyond the Cognitive-Situative Divide and Combining Individual and Social Processes”, Educational psychologist: official publication of the Division of Educational Psychology of the American Psychological Association, 45 (1), 2010, pp. 15–28.
8.) Tom Anderson, Melody K. Milbrandt, Art for life: Authentic Instruction in Art. New York 2005.
[Dieser Text findet sich im Reader Nr. 2 auf S. 120.]